Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tashiro, Shinsuke; Abe, Hitoshi
JAEA-Technology 2015-044, 20 Pages, 2016/03
In order to estimate public dose under a criticality accident in fuel solution of a fuel reprocessing plant, release behavior of radioiodine from the fuel solution to atmosphere is very important. In this report, time evolution of  I concentration in gas phase of TRACY core tank was measured until the concentration in the solution decreased. Furthermore, cumulative release ratio (CRR) and release rate (RR) from the solution to the atmosphere of radioiodine were evaluated by applying previously-reported evaluation model. As a result, for the case of short transient criticality, RR of
I concentration in gas phase of TRACY core tank was measured until the concentration in the solution decreased. Furthermore, cumulative release ratio (CRR) and release rate (RR) from the solution to the atmosphere of radioiodine were evaluated by applying previously-reported evaluation model. As a result, for the case of short transient criticality, RR of  I became maximum at 1 hour later from the ending and almost constant after 8 hour later. Furthermore, relationship of each elapsed time between total fission number and release rate of
I became maximum at 1 hour later from the ending and almost constant after 8 hour later. Furthermore, relationship of each elapsed time between total fission number and release rate of  I could be derived. On the other hand, for the case of long criticality excursion, such as JCO criticality accident, the CRR and RR of radioiodine increased monotonously with time.
I could be derived. On the other hand, for the case of long criticality excursion, such as JCO criticality accident, the CRR and RR of radioiodine increased monotonously with time.
Katayama, Kazunari*; Ushida, Hiroki*; Matsuura, Hideaki*; Fukada, Satoshi*; Goto, Minoru; Nakagawa, Shigeaki
Fusion Science and Technology, 68(3), p.662 - 668, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:79.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tritium production utilizing nuclear reactions by neutron and lithium in a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor is attractive for development of a fusion reactor. From viewpoints of tritium safety and production efficiency, tritium confinement technique is an important issue. It is known that alumina has high resistance for gas permeation. In this study, hydrogen permeation experiments in commercial alumina tubes were conducted and hydrogen permeability, diffusivity and solubility was evaluated. By using obtained data, tritium permeation behavior from an Al O
O -coated Li-compound particle was simulated. Additionally, by using literature data for hydrogen behavior in zirconium, an effect of Zr incorporation into an Al
-coated Li-compound particle was simulated. Additionally, by using literature data for hydrogen behavior in zirconium, an effect of Zr incorporation into an Al O
O coating on tritium permeation was discussed. It was indicated that the majority of produced tritium was released through the Al
coating on tritium permeation was discussed. It was indicated that the majority of produced tritium was released through the Al O
O coating above 500
coating above 500 C. However, it is expected that total tritium leak is suppressed to below 0.67% of total tritium produced at 500
C. However, it is expected that total tritium leak is suppressed to below 0.67% of total tritium produced at 500 C by incorporating Zr fine particles into the inside of Al
C by incorporating Zr fine particles into the inside of Al O
O coating.
coating.
 -mode plasmas in JT-60U tokamak
-mode plasmas in JT-60U tokamakUrano, Hajime; Takizuka, Tomonori; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Miura, Yukitoshi; Kamada, Yutaka
Nuclear Fusion, 46(8), p.781 - 787, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:58.85(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The degradation of energy confinement with increased toroidal beta 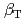 was shown by the non-dimensional analysis in JT-60U. The dependence of the energy confinement on
was shown by the non-dimensional analysis in JT-60U. The dependence of the energy confinement on 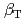 was examined by both the JT-60U ELMy
was examined by both the JT-60U ELMy 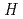 -mode confinement database and the dedicated experiment on a single
-mode confinement database and the dedicated experiment on a single 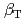 scan while
scan while 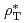 and
and 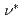 were kept fixed as well as the other magnetic geometrical parameters. In both cases, the degradation of energy confinement with increasing
were kept fixed as well as the other magnetic geometrical parameters. In both cases, the degradation of energy confinement with increasing 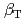 was observed, satisfying the relation of
was observed, satisfying the relation of 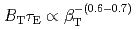 . This dependence is a little weaker than that predicted by the IPB98(y,2) scaling. The fusion power production rate was estimated to increase in proportion to
. This dependence is a little weaker than that predicted by the IPB98(y,2) scaling. The fusion power production rate was estimated to increase in proportion to 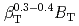 .
.
Takizuka, Tomonori; Urano, Hajime; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(6), p.799 - 806, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:48.35(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dependence of the ELMy H-mode confinement on the beta has been investigated for a long time, but a common conclusion has not yet been obtained.The IPB98(y,2) scaling shows a strong degradation with beta, while DIII-D and JET experiments exhibited the absence of the beta degradation. Recent JT-60U experiment demonstrated that the strong beta degradation really exists for the ELMy H-mode. In the present paper, we analyze the JT-60U ELMy H-mode confinement database and confirm the strong power degradation of the confinement time, which corresponds to the strong beta degradation consistent with the above result. We analyze also the ITPA H-mode confinement database in detail. How the beta dependence of the confinement time is changed by the externally given parameters, such as the shape parameters, are investigated.
 plasma operation
plasma operationTamai, Hiroshi; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujita, Takaaki; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ichimura, Makoto*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(12), p.1676 - 1683, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:45.53(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Design studies are shown on the National Centralized Tokamak facility. The machine design is carried out to investigate the capability for the flexibility in aspect ratio and shape controllability for the demonstration of the high-beta steady state operation with nation-wide collaboration, in parallel with ITER towards DEMO. Two designs are proposed and assessed with respect to the physics requirements such as confinement, stability, current drive, divertor, and energetic particle confinement. The operation range in the aspect ratio and the plasma shape is widely enhanced in consistent with the sufficient divertor pumping. Evaluations of the plasma performance towards the determination of machine design are presented.
Stober, J.*; Lomas, P. J.*; Saibene, G.*; Andrew, Y.*; Belo, P.*; Conway, G. D.*; Herrmann, A.*; Horton, L. D.*; Kempenaars, M.*; Koslowski, H.-R.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(11), p.1213 - 1223, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:76.37(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Ninomiya, Hiromasa
Nuclear Fusion, 45(10), p.S13 - S31, 2005/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper summarizes the results presented at the 20th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference 2004 in the sessions of confinement, plasma-wall interaction and innovative confinement concept. The highlights of the presentations are as follows. Long pulse operation with high beta and high bootstrap fraction much longer than the current diffusion time has been achieved. The discharge scenario optimization and its extrapolation towards ITER have progressed remarkably. Significant progress has been made in understanding of global confinement and transport physics.
 and collisionality approaching ITER conditions
and collisionality approaching ITER conditionsCordey, J. G.*; Thomsen, K.*; Chudnovskiy, A.*; Kardaun, O. J. W. F.*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Snipes, J. A.*; Greenwald, M.*; Sugiyama, L.*; Ryter, F.*; Kus, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(9), p.1078 - 1084, 2005/09
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:82.4(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The condition of the latest version of the ELMy H-mode database has been re-examined. It is shown that there is bias in the ordinary least squares regression for some of the variables. To address these shortcomings three different techniques are employed: (a)principal component regression, (b)an error in variables technique and (c)the selection of a better conditioned dataset with fewer variables. Scalings in terms of the dimensionless physics valiables, as well as the standard set of engineering variables, are derived. The new scalings give a very similar performance for existing scalings for ITER at the standard beta, but a much improvement performance at higher beta.
Kamiya, Kensaku; Oyama, Naoyuki; Miura, Yukitoshi; Hubbard, A. E.*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 46(11), p.1745 - 1755, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:40.22(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Recent experiments in the JFT-2M tokamak have concentrated on the studies of the access condition for the H-mode operation without any large ELMs, namely High Recycling Steady (HRS) H-mode regime in terms of the pedestal parameters. The HRS regime is more likely at the higher edge density and lower edge temperature, while the ELMy H-mode having large ELMs appears at the lower edge density and higher edge temperature. It is found that the ELMy/HRS operational boundary occurs at the normalized electron collisionality of  *
*
 1 in the plasma edge region, depending slightly on q
1 in the plasma edge region, depending slightly on q . A key feature of the HRS H-mode is the presence of the coherent magnetic fluctuations in the frequency range of the order of 10-100 kHz. It is suggested that the edge MHD activities may keep an edge pressure below a certain level needed to induce a large ELM.
. A key feature of the HRS H-mode is the presence of the coherent magnetic fluctuations in the frequency range of the order of 10-100 kHz. It is suggested that the edge MHD activities may keep an edge pressure below a certain level needed to induce a large ELM.
Shimada, Michiya; Campbell, D.*; Stambaugh, R.*; Polevoi, A. R.*; Mukhovatov, V.*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Costley, A. E.*; Donn , A. J. H.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Federici, G.*; et al.
, A. J. H.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Federici, G.*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2004) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/11
This paper summarises recent progress in the physics basis and its impact on the expected performance of ITER. Significant progress has been made in many outstanding issues and in the development of hybrid and steady state operation scenarios, leading to increased confidence of achieving ITER's goals. Experiments show that tailoring the current profile can improve confinement over the standard H-mode and allow an increase in beta up to the no-wall limit at safety factors  4. Extrapolation to ITER suggests that at the reduced plasma current of
4. Extrapolation to ITER suggests that at the reduced plasma current of  12MA, high Q
12MA, high Q  10 and long pulse (
10 and long pulse ( 1000 s) operation is possible with benign ELMs. Analysis of disruption scenarios has been performed based on guidelines on current quench rates and halo currents, derived from the experimental database. With conservative assumptions, estimated electromagnetic forces on the in-vessel components are below the design target values, confirming the robustness of the ITER design against disruption forces.
1000 s) operation is possible with benign ELMs. Analysis of disruption scenarios has been performed based on guidelines on current quench rates and halo currents, derived from the experimental database. With conservative assumptions, estimated electromagnetic forces on the in-vessel components are below the design target values, confirming the robustness of the ITER design against disruption forces.
Kamiya, Kensaku; Bakhtiari, M.; Kasai, Satoshi; Kawashima, Hisato; Kusama, Yoshinori; Miura, Yukitoshi; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Oyama, Naoyuki; Sato, Masayasu; Shinohara, Koji; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 46(5A), p.A157 - A163, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:56.48(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A new operating regime, High Recycling Steady (HRS) H-mode regime, has been discovered on JFT-2M, which is easily reproduced under the wall fueling from the boronized first wall. Accompanying the HRS H-mode transition, the coherent magnetic and floating potential fluctuations are seen on magnetic probes at vessel wall and Langmuir probe in SOL, respectively. These coherent fluctuations have a frequency of the order of 10-100 kHz with significant variation, which is recognized to be important to enhance the particle transport. The HRS can be seen even at 

 3 with
3 with 
 /
/
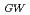
 0.4 for the fixed delta
0.4 for the fixed delta 0.4 in the standard single-null divertor configuration. Recent experimental results from JFT-2M show that the plasma shape also seems to play an important role in determining the type of ELMs. The HRS regime can be extended up to delta
0.4 in the standard single-null divertor configuration. Recent experimental results from JFT-2M show that the plasma shape also seems to play an important role in determining the type of ELMs. The HRS regime can be extended up to delta 0.75 and
0.75 and 

 2.6 in the double-null configuration, while lower delta boundary exists at delta
2.6 in the double-null configuration, while lower delta boundary exists at delta 0.3 with moderate
0.3 with moderate 

 4 even at high recycling and/or density condition of
4 even at high recycling and/or density condition of 
 /
/
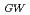
 0.4.
0.4.
Li, J.; Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Physics of Plasmas, 11(4), p.1493 - 1510, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:85.33(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The electron temperature gradient (ETG) driven turbulence in tokamak core plasmas is numerically investigated based on three-dimensional gyrofluid model with adiabatic ion response. Attentions are focused on the zonal flow dynamics in ETG fluctuations and the resultant electron heat transport. A high electron energy confinement mode is found in the weak magnetic shear regime, which is closely relevant with self-organization behavior of turbulence through the enhanced zonal flow dynamics rather than the weak shear stabilization of ETG fluctuations. It is demonstrated that the weak shear is favorable for the enhancement of zonal flows in ETG turbulence.
JT-60 Team
JAERI-Review 2003-029, 197 Pages, 2003/11
no abstracts in English
Kubo, Hirotaka; Sakurai, Shinji; Higashijima, Satoru; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Itami, Kiyoshi; Konoshima, Shigeru; Nakano, Tomohide; Koide, Yoshihiko; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 313-316(1-3), p.1197 - 1201, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:75.79(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Higashijima, Satoru; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Hirotaka; Miura, Yukitoshi; Nakano, Tomohide; Konoshima, Shigeru; Itami, Kiyoshi; Sakurai, Shinji; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Tamai, Hiroshi; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 313-316, p.1123 - 1130, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:72.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Reduction of steady-state heat load in the divertor and transient one by ELMs is a crucial issue for tokamak fusion devices. High radiation loss power is necessary for the heat load reduction, and the conventional gas puffing can increase the density and the radiation loss power, but it degrades the confinement. Core plasma with high confinement should be maintained simultaneously. Impurity seeding is a secure way to enhance the radiation loss power. In JT-60U, heat load is successfully reduced by Ar injection with keeping a high confinement in ELMy H-mode plasmas. In this paper, heat load reduction, radiation enhancement, and change of ELM activity are discussed.
Yoshida, Hiroshi; Glugla, M.*; Hayashi, Takumi; L sser, R.*; Murdoch, D.*; Nishi, Masataka; Haange, R.*
sser, R.*; Murdoch, D.*; Nishi, Masataka; Haange, R.*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 61-62, p.513 - 523, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:84.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)ITER tritium plant is composed of tokamak fuel cycle systems, tritium confinement and detritation systems. The tokamak fuel cycle systems, composed of various tritium sumsystems such as vacuum vessel cleaning gas processing, tokamak exhaust processing, hydrogen isotope separation, fuel storage, mixing and delivery, and external tritium receiving and long-term storage, has been designed to meet not only ITER operation scenarios but safety requirements (minimization of equipment tritium inventory and reduction of environmental tritium release at different off-normal events and accident scenarios). Multiple confinement design was employed because tritium easily permeates through metals (at  150
150  C) and plastics (at ambient temperature) and mixed with moisture in room air. That is, tritium process equipment and piping are designed to be the primary confinement barrier, and the process equipments (tritium inventory
C) and plastics (at ambient temperature) and mixed with moisture in room air. That is, tritium process equipment and piping are designed to be the primary confinement barrier, and the process equipments (tritium inventory  1 g) are surrounded by the secondary confinement barrier such as a glovebox. Tritium process rooms, which contains these facilities, form the tertiary confinement barrier, and equipped with emergency isolation valves in the heating ventillation and air conditioning ducts as well as atmosphere detritiation systems. This confinement approach has been applied to tokamak building, tritium building, and hotcell and radwaste building.
1 g) are surrounded by the secondary confinement barrier such as a glovebox. Tritium process rooms, which contains these facilities, form the tertiary confinement barrier, and equipped with emergency isolation valves in the heating ventillation and air conditioning ducts as well as atmosphere detritiation systems. This confinement approach has been applied to tokamak building, tritium building, and hotcell and radwaste building.
 superconducting tube
superconducting tubeYamauchi, Toshihiko; Matsuzawa, Hidenori*; Mikami, Koji*; Ishikawa, Junichi*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 41(9), p.5799 - 5800, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.64(Physics, Applied)This paper describes the experimental result of the interaction between a high-Tc superconductor and charged particles (plasma). This study is expected for the interaction between the charged particle and superconductor in the group, high-Tc superconducting wiggler for electron beam of FEL (collaboration with Prof.Matsuzawa) and high-Tc superconducting tube for beam guiding published in the journal "Nature".
Kubo, Hirotaka; JT-60 Team
Physics of Plasmas, 9(5), p.2127 - 2133, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:50.83(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Yoshikawa, Kiyoshi*; Inoue, Nobuyuki*; Yamazaki, Tetsuo*; Makino, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Yasushi*; Toku, Hisayuki*; Masuda, Kai*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Onishi, Masami*; Horiike, Hiroshi*; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2002-020, 63 Pages, 2002/03
no abstracts in English
Yamazaki, Kozo*; Kikuchi, Mitsuru
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.5, p.28 - 35, 2002/00
Plasma operational boundaries of tokamak and helical systems are surveyed and compared with each other. Global confinement scaling lawas are similar and gyro-Bohm like, however, local transport process is different due to sawtooth oscillations in tokamaks and ripple transport loss in helical systems.for stability limit, achievable tokamak beta is explained by ideal or resistive MHD theories. beta values. On the other hand, beta values in helical system are beyond Mercier mode limit.